As Rosetta approaches the surface of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, the Comet Pressure Sensor (COPS) on the ROSINA instrument is measuring the gas pressure around the nucleus increasing!
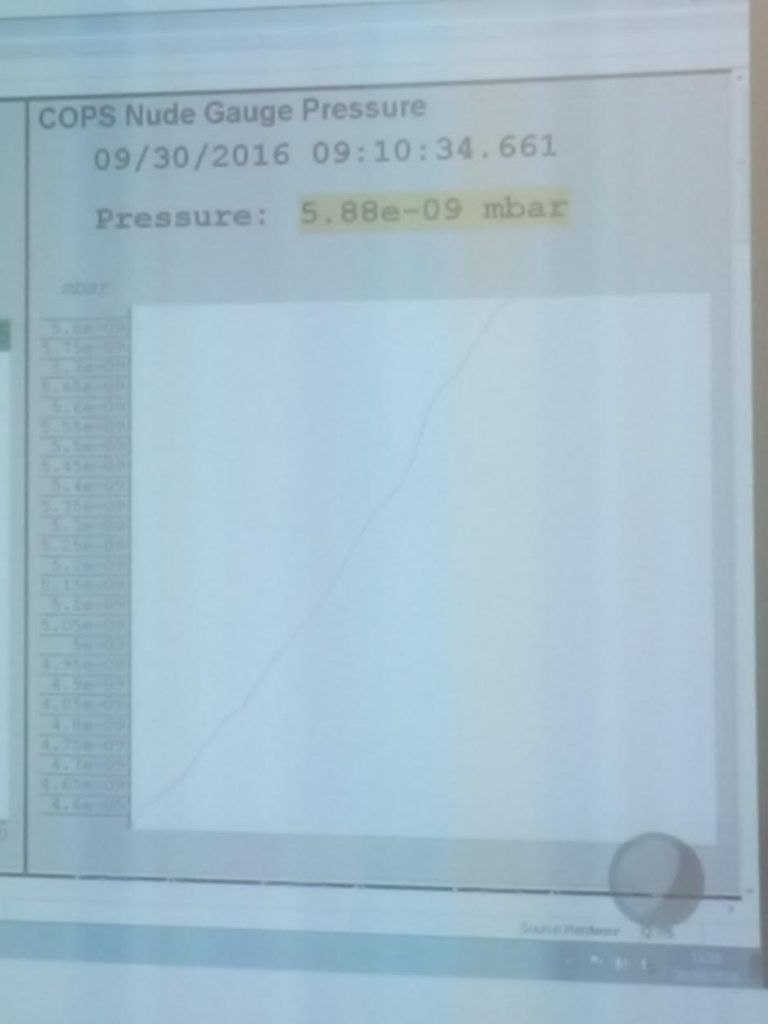
The ROSINA-COPS readings on 30 September 2016. Image courtesy K. Altwegg.








Discussion: 8 comments
Thank you, Rosetta. Say Hi and thank you to Philea for us down here. What an incredible journey!! We will miss you all.
The significance of this is ? ( for the lay community watching
@Rich,
It is just to confirm that, as expected, the coma closer to the nucleus is denser. This is the same as you would get on Earth, with higher atmospheric density at sea level, as opposed to say 10 km.
Thanks ian for the answer. One more question : Were several (pression / altitude) measures published or was this the only picture realesed by the team as per now ?
Thanks in advance for your reply.
@Serge,
I have no specific information on that, but would expect that the COPS instrument was turned on all the way down to the surface. Therefore I would surmise that they have readings for the whole of the descent.
I imagine it will be included in a future paper. The raw data may be made available through the ESA planetary science archive at some point, I’m guessing:
ftp://psa.esac.esa.int/pub/mirror/INTERNATIONAL-ROSETTA-MISSION/
It will be part of the ROSINA dataset.
Rich.
The gas and ion cloud around the comet – the coma – is produced by out gassing of material from the comet. Sublimation basically. So measuring the pressure gives you information about the density and extent of that gas cloud, and about material love SS from the comet.
It’s worth pointing out though that the pressure indicated is EXTREMELY low. 5.88*10^-9mBar is far lower than the pressure even in an laboratory ultra-high-vacuum chamber. To achieve that sort of pressure requires highly specialised pumps, an extremely clean system, all metal seals (no rubber or plastic) and baking the whole system to typically 300C. Usually a purpose built oven is built round the chamber.
Atmospheric pressure at sea level on earth is about one bar. So it is 5.88*10^-12Bar, or roughly six million millionths of a Bar, or 0.00000000000588Bar!
Wow, Harvey, fascinating!
The bigger the voids The more sterile. Comets are daughters of Silence.