ESA’s space weather services website (https://swe.ssa.esa.int) has deployed three new servicesproviding information and data to the space weather user community. These are:
- 24-hour forecasts of major solar flares
- Tailored services designed to support resource exploitation in the Arctic region
- A new version of the AVIDOS application for aviation users, now taking into account solar events
This is very good news because in one update, the Space Situational Awareness programme team have increased the range of products available via all four ESA SSA SWE Expert Service Centres.
Read below for detailed descriptions of the new services.
Questions? Contact the SSA space weather team
A-EFFort
- 24-hour forecasts of major solar flares, developed by the Academy of Athens
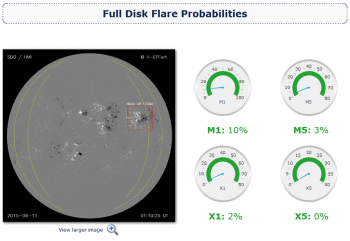 Athens Effective Solar Flare Forecasting (A-EFFort) is an on-line solar-flare prediction service that monitors, evaluates and provides advance warning of intense solar flare activity. It comprises a web-based interface and an automated flare forecasting tool relying on the effective connected magnetic field strength of eligible active regions identified in full-disk SDO/HMI line-of-sight magnetogram data.
Athens Effective Solar Flare Forecasting (A-EFFort) is an on-line solar-flare prediction service that monitors, evaluates and provides advance warning of intense solar flare activity. It comprises a web-based interface and an automated flare forecasting tool relying on the effective connected magnetic field strength of eligible active regions identified in full-disk SDO/HMI line-of-sight magnetogram data.
The service provides probabilities for major flares on full disk and on individual active regions. Probabilities are effective immediately, valid for a 24-hour forecast window and refreshed every three hours.
Users can access the service via the SWE portal and also register for email alerts. A-EFFort was developed by the Research Centre for Astronomy and Applied Mathematics, Academy of Athens
RESOSS
- Tailored services designed to support resource exploitation, developed by TGO and NMA
https://swe.ssa.esa.int/web/guest/geomagnetic-conditions
https://swe.ssa.esa.int/web/guest/ionospheric-weather
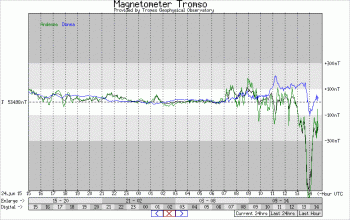 The service for Resource Exploitation System Operators (RESOSS) builds on existing commercial and non-commercial components that are presently associated with two different SSA Expert Service Centres: the Geomagnetism ESC and the Ionosphere ESC. This separation is due to the fact that information on geomagnetic disturbances and precise positioning are delivered by different providers. The services target users working in the fields of directional wellbore drilling and aeromagnetic surveying.
The service for Resource Exploitation System Operators (RESOSS) builds on existing commercial and non-commercial components that are presently associated with two different SSA Expert Service Centres: the Geomagnetism ESC and the Ionosphere ESC. This separation is due to the fact that information on geomagnetic disturbances and precise positioning are delivered by different providers. The services target users working in the fields of directional wellbore drilling and aeromagnetic surveying.
The oil industry today makes extensive use of geomagnetic data in support of directional drilling, and magnetic survey instruments are commonly used for navigation. To support drill operation, the field direction should be known to high accuracy. In the North Sea, the direction of Earth’s magnetic field may change by 0.2 degrees during a normal day and by much more during a geomagnetic storm. Reference monitoring of the magnetic field therefore provides crucial information to support these activities.
Geomagnetic surveying – from the air as well as the sea – in most cases requires very accurate time-dependent reference magnetic field data. Companies or organisations carrying out magnetic surveys benefit from the use of space weather information. Forecasts as well as real-time and archived reference data may provide valuable information in support of both campaign planning and post-survey data analysis.
In RESOSS, near real-time information about geomagnetic and ionospheric disturbances is unified into one service.
The service is accessed through a main web page, where the user has three options: accessing a dedicated service for geomagnetic surveying or for directional drilling, or accessing a registration page for receiving geomagnetic alerts meant for both domains.
RESOSS was developed by Tromsø Geophysical Observatory and the Norwegian Mapping Authority.
AVIDOS v2.0
- AVIDOS is informational and educational online software for the assessment of galactic cosmic radiation exposure at flight altitudes.
The radiation environment at aircraft altitude is slightly increased with respect to that at ground level due to reduced atmospheric shielding from incident galactic cosmic rays, the flux of which varies with the solar cycle. In addition, during severe particle storms resulting from sporadic solar activity, aircraft in the polar regions or flying at high altitude may additionally experience increased radiation doses. Although well below dangerous levels in all cases, European legislation is in place identifying aircrew as radiation workers and their annual expected exposure is recorded. Individual airlines may also take action to modify their flight routes in case of a severe radiation storm or perceived impact of space weather on safety critical systems such as communications.
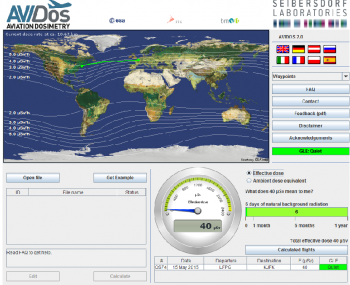 AVIDOS calculates the effective dose between 8 km and 15 km of altitude, for any geographic location and for an entire 11-year cycle of solar activity. The application employs a multi-parameter model built using Monte Carlo simulations of cosmic radiation exposure. The models used have been validated by numerous measurements on board aircraft.
AVIDOS calculates the effective dose between 8 km and 15 km of altitude, for any geographic location and for an entire 11-year cycle of solar activity. The application employs a multi-parameter model built using Monte Carlo simulations of cosmic radiation exposure. The models used have been validated by numerous measurements on board aircraft.
With this update to the application, AVIDOS now provides an estimate of the radiation dose at aircraft altitude due to solar storms. It assumes different scenarios resulting in a range of route dose estimates for a flight taking place during a solar storm.
AVIDOS v2.0 was developed by Seibersdorf.


Discussion: no comments