Over the past few days, engineers assembled the Service Module for Artemis III, made of the third European Service Module connected to the Crew Module Adapter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, USA. Once they will attach it to the Crew Module and solar array wings next year, the Orion spacecraft will be complete.
The Orion spacecraft consists of two main components: the Crew Module, which serves as the habitat for up to four astronauts and cargo, and the European Service Module (ESM), responsible for propulsion, power and life support. The ESM connects to the Crew Module through the Crew Module Adapter (CMA), which manages the electrical, fluid and data systems between these two modules.
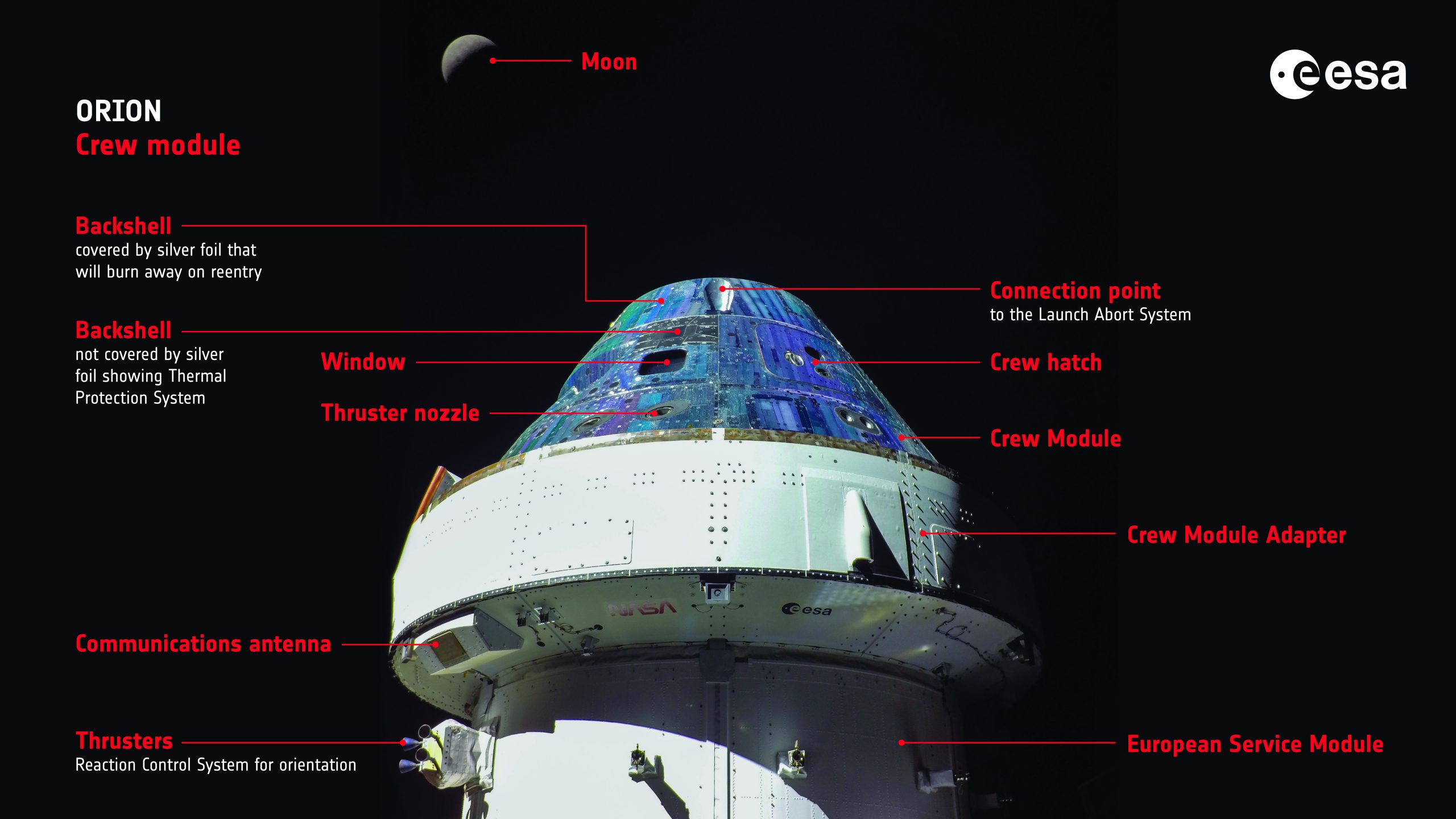
Components of the Orion vehicle, using a photo from Artemis I.
Credit: ESA/K. Lochtenberg
The recent assembly process involved carefully suspending the CMA, while lifting the ESM very, very, slowly, stopping regularly to check the alignment using precise laser measurements. The ESM is placed on a mobile platform that allows engineers to accurately move the precious module with six degrees of freedom – x, y, z and three rotations – to ensure an exact alignment.
Once the modules are ready to be fastened, engineers install 192 screws all around the modules, one by one, an extremely delicate process. Some of these fastenings are particularly challenging to reach, requiring special precautions like foil to prevent parts from falling into the module underneath.
What’s next?
Now that the physical connection between the ESM and CMA is complete, the next steps include welding operations to connect the propulsion and consumable systems which are crucial for the environmental control and life support system (ECLSS) as they ensure breathable air, water and temperature regulation inside the spacecraft. The combined Service Module will undergo rigorous proof pressure testing to confirm that all systems are leak-proof and to ensure a secure connection before the spacecraft moves on to further assembly stages.
Stay tuned!
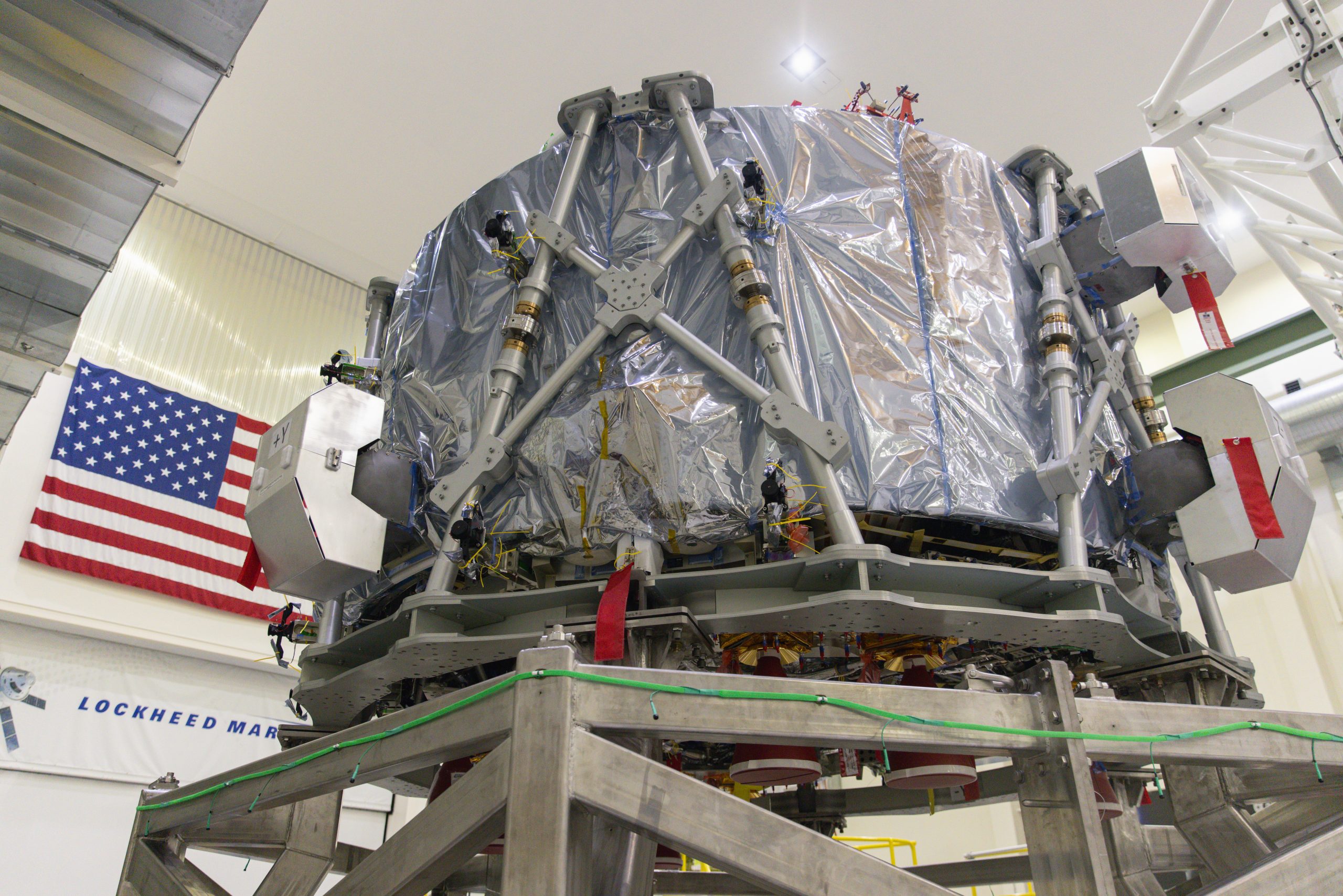

The third European Service Module at the Kennedy Space Center before being the connection procedure.
Credit: NASA/F. Michaux
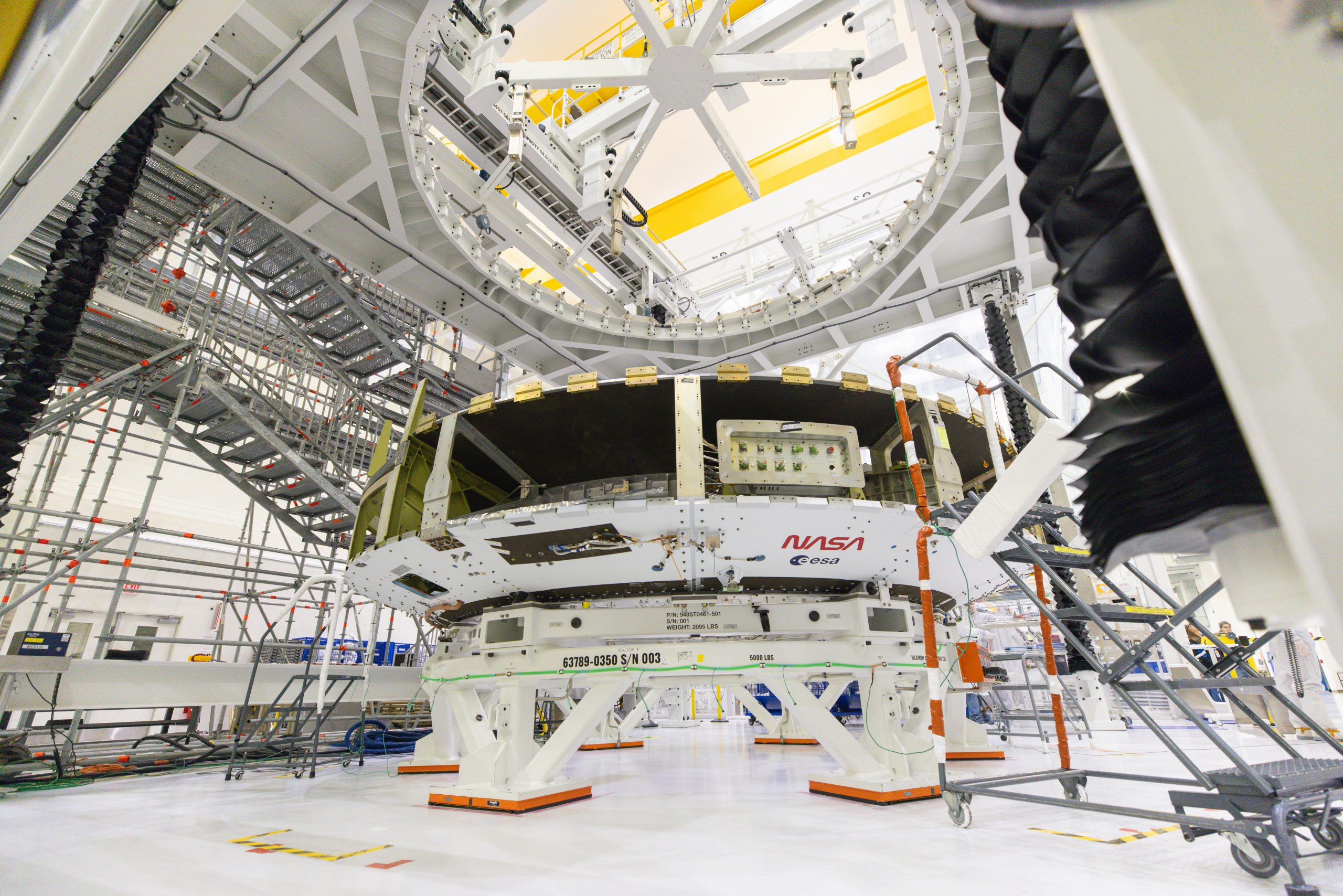

The Crew Module Adapter with the NASA and ESA logos at the Kennedy Space Center before being the connection procedure.
Credit: NASA/F. Michaux
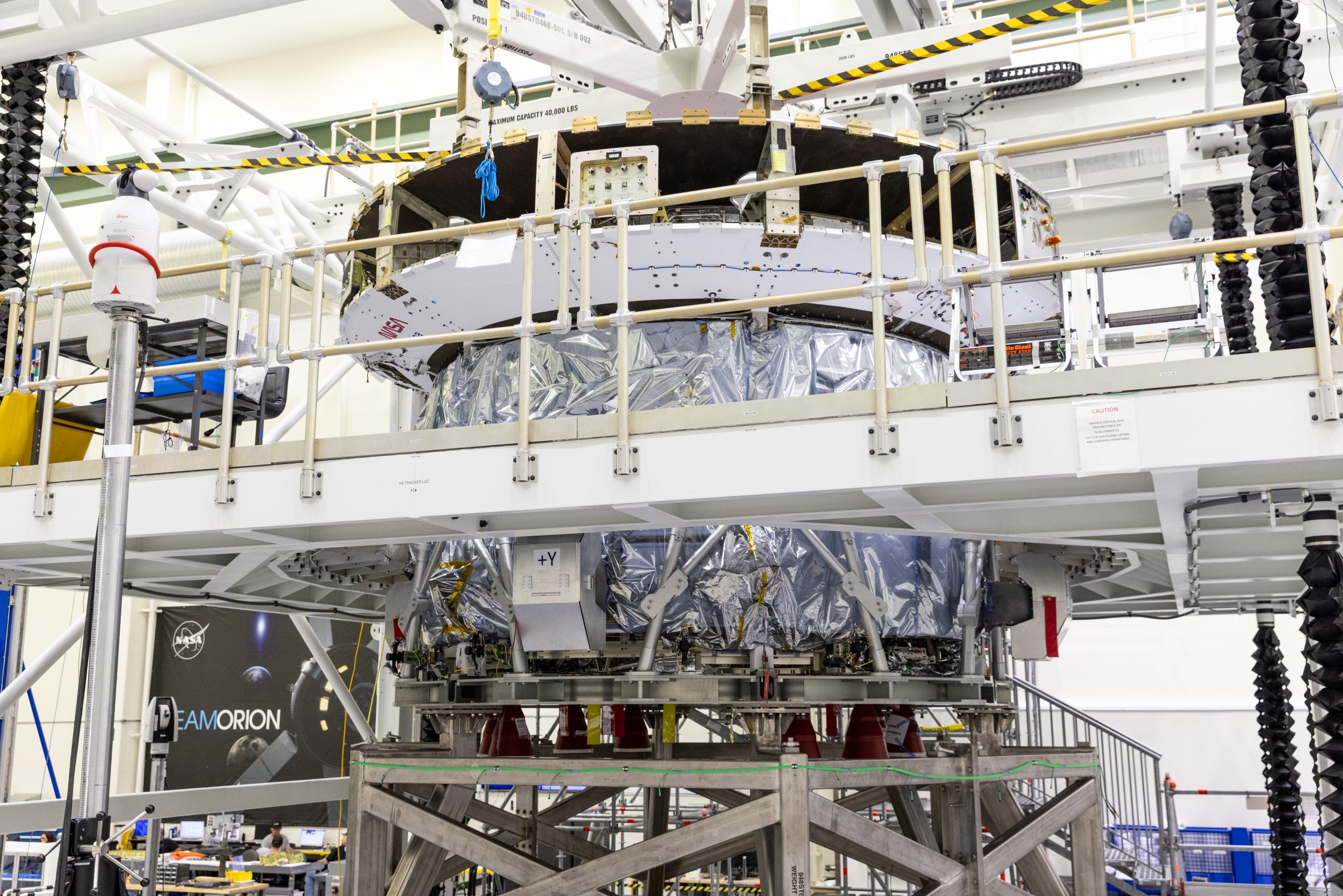

On Tuesday 24 September, teams at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center began connecting ESA’s third European Service Module, assembled by Airbus in Bremen, Germany, to the Crew Module Adapter, completing the Service Module that will supply propulsion, thermal control, and electrical power for NASA’s Orion spacecraft on the Artemis III mission.
Credit: NASA/K. Shiflett
 Automated Transfer Vehicle page
Automated Transfer Vehicle page ATV blog archive
ATV blog archive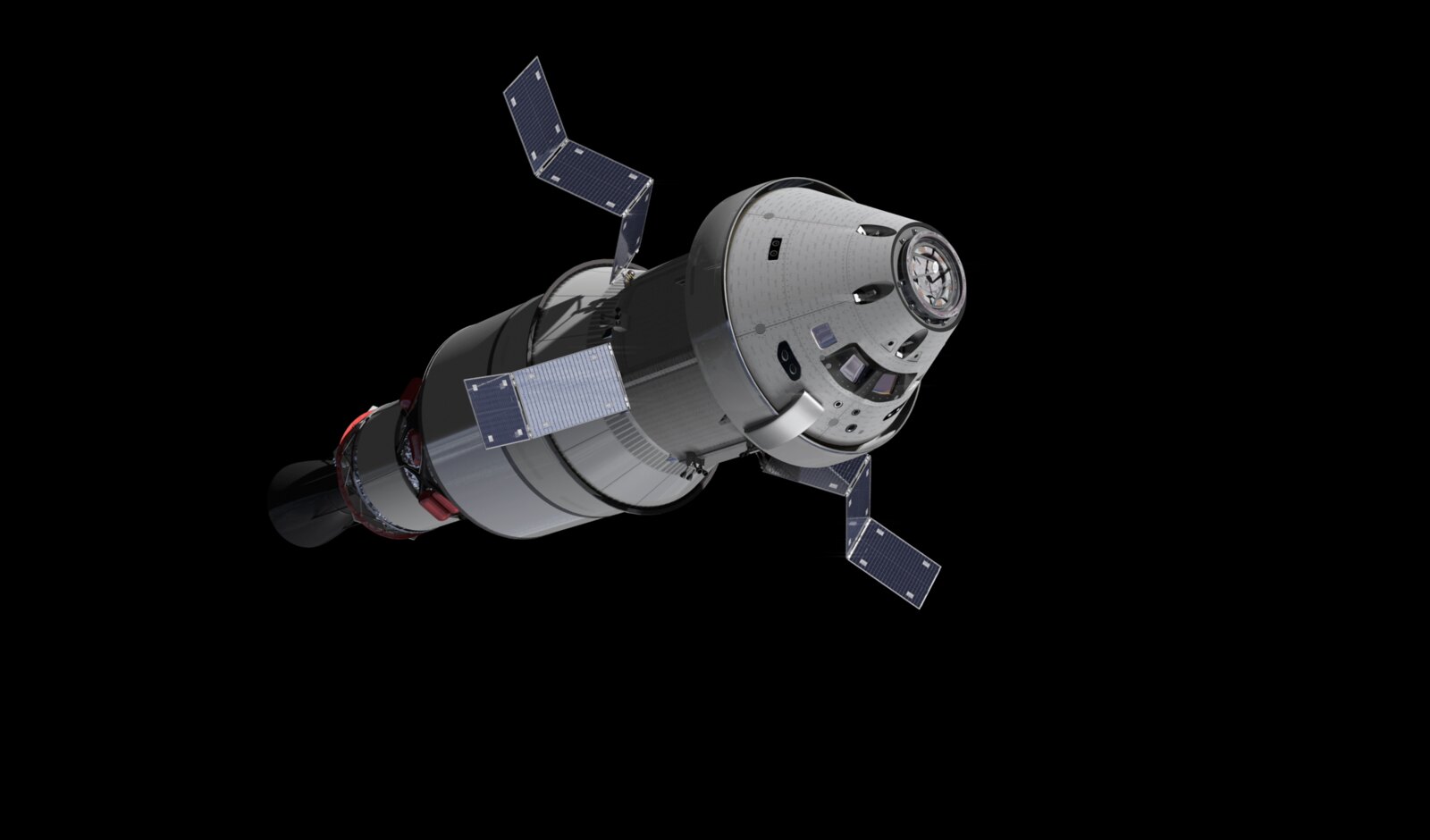
Discussion: no comments